DAO 正处于起步阶段,理论研究尚处于空白,且难以实现大规模应用。本文首次系统地提出 DAO 五层分析框架。
DAO is in the initial stages, and theoretical research is in a state of vacuum and difficult to achieve on a large scale. For the first time, the DAO five-tier analysis framework is presented systematically.
摘 要:分布式自治并非一个新的概念,自然界中的自组织现象、互联网上的动态网民群体组织以及分布式人工智能等均可视作其早期表现形式。近年来,区块链技术的快速发展催生了去中心化自治组织(DAO),它是一种将组织的管理和运营规则以智能合约的形式编码在区块链上,从而在没有集中控制或第三方干预的情况下自主运行的组织形式。因此,DAO 有望成为应对不确定、多样、复杂环境的一种新型有效组织。然而,DAO 正处于起步阶段,理论研究尚处于空白,且难以实现大规模应用。本文首先对 DAO 的概念及特征做出清晰界定;接着首次系统地提出 DAO 五层分析框架,并以此为基础对典型的 DAO 应用案例——Aragon 做了详尽分析;之后讨论DAO 目前所面临的问题和下一步可能的研究方向,以期为未来研究提供有益的参考与借鉴。
In recent years, the rapid development of block-chain technology has given rise to decentralised self-governing organizations (DAOs), a form of organization that encodes the organization's management and operation rules in the form of smart contracts on the block chain, thus operating autonomously without centralized control or third-party intervention. Therefore, DAO is expected to be a new type of effective organization for dealing with uncertain, diverse and complex environments. However, DAO is in the initial stages, and theoretical research is still lacking and difficult to achieve on a large scale. This paper begins with a clear definition of DAO concepts and characteristics; it is followed by the first systematic presentation of the DAO five-tier analysis framework, based on which the typical DAO application case, Aragon, is analysed in detail; it then discusses the problems currently faced by DAO and possible next research directions, with a view to providing useful references and lessons for future research.


关键词:去中心化自治组织;智能合约;智能化管理;平行区块链
Keywords: decentralised self-governing organizations; smart contracts; intelligent management; parallel block chains
引用格式:丁文文,王帅,李娟娟,袁勇,欧阳丽炜,王飞跃. 去中心化自治组织:发展现状、分析框架与未来趋势[J]. 智能科学与技术学报, 2019, 1(2): 202-213.
Quoted format: Dingwen, King, Lee, Yuan Yong, Ouyang Li, Wang Fei-jian, Wang Fei-jian. To centralize Autonomous Organizations: Current Development, Analysis Framework and Future Trends [J]. Journal of Smart Science and Technology, 2019, 1(2): 202-213.
随着信息技术的发展以及组织自身复杂性的不断增加,传统组织的雇佣关系、管理模式等已经很难适应复杂多变的环境以及新一代个体对组织的要求。去中心化自治组织 (decentralized au- tonomous organization,DAO)将去中心化、自主、自治与通证经济激励相结合,将系统内的各个元素作为资产,使得货币资本、人力资本以及其他要素资本充分融合,从而更好地激发组织的效能并实现价值流转,为解决现有的组织管理问题提供了很好的思路。然而,DAO 并非一个全新的概念,自然界中的自组织现象、互联网中的动态网民群体组织(cyber movement organizations,CMOs)以及人工智能的重要分支——分布式人工智能(distributed artificial intelligence,DAI)等均可认为是 DAO 的雏形,这些都为其出现奠定了理论及现实基础。
With the development of information technology and the growing complexity of the organization, it has become difficult for traditional organizations to adapt their employment relationships, management models, etc., to complex and changing environments and the demands of new generations of individuals on the organization. Decentralized autonomous organizations (decentralized au-tonomous organization, DAO) combine centralization, autonomy, autonomy, and economic incentives across the system as assets that allow for the full integration of monetary capital, human capital, and other elements of capital in order to better stimulate organizational effectiveness and value flow, providing good ideas to address existing organizational management problems.
自组织现象(self-organization phenomenon)是自然界中极为普遍的现象,它是由生物个体之间的协同交互所导致的。在交互的过程中,每个个体都自发地倾向于从无序的运动到由个体之间关联而引起的协调合作的运动[1]。例如,蚁群、蜂群、鸟群及菌落等在生物系统中的聚集、迁移、合作觅食等众多涌现行为[2],完全是局部相互作用的结果, 不存在集中控制。
The phenomenon of self-organization (self-organization phenomenon) is very common in nature and is the result of a synergistic interaction between individual organisms. In the process of interaction, each individual automatically tends to move from disorderly motion to a coordinated cooperative movement resulting from individual connections [1]. For example, there is an accumulation of ants, bees, birds and communities in the biological system, which is currently the result of[2], which is entirely a local interaction, and there is no centralized control.
自组织现象的充分开放、自主交互、去中心化控制、复杂多样以及涌现等特点,不仅为 DAO 的出现奠定了思想雏形,也推动了各个学科的发展。如 1959 年 Grasse 对蚁群筑巢和觅食行为进行了研究[3],他将这一现象称为"stigmerge",后来被很多其他的自组织系统所借鉴[4]。自组织系统目前被用于解决那些中心化控制难以解决的问题,如普适计算的海量数据处理[5]、P2P 网络中的服务欺骗和节点资源滥用问题[6]、数据库管理中的数据存储问题[7]等。自组织理论群及系统则为后期 DAO 的落地提供了理论基础。从 20 世纪 70 年代开始,布鲁塞尔自由大学的 Prigogine教授从热力学角度对自组织系统能量的吸收和耗散与组织有序之间的关系进行了研究,创立了耗散结构理论[8],该理论对于理解复杂组织系统的自组织演化具有重要意义。随后人们又从不同的角度对自组织现象进行了研究, 形成了以耗散结构论、系统学、超循环论、混沌和分形等为代表的自组织理论群。
Since the beginning of the twentieth century and beginning with the 1970s, Professor Prigogine of the Free University of Brussels has studied the relationship between the absorption and depletion of the energy of the system and the organization, and has developed the theory of fragmentation, the theory of fragmentation of the structure, which is important for the understanding of complex organizational systems.
在互联网层面,移动互联网和移动智能设备的普及使得网络虚拟世界成为人们日常活动的重要空间,并催生了大规模 CMOs[9]。CMOs 是指由事件或目标引导,短期内聚集在一起,参与、讨论并共同实施某些社会行为的在线网民群体[10]。人肉搜索[11-12]、水军[13]、众包[14]等都是典型的 CMOs。与自然界中的自组织现象不同,虚拟空间中的 CMOs 不受现实物理世界的空间限制,演化过程由事件或目标驱动,快速形成、传播且高度互动,并伴随着目标的消失而自动解散。例如,众包现象就是由任务驱动,在某一特定时间出现在网络中且具有明显互动的结构及目标引导的局部中心,随着任务的完成,中心消失,取而代之的是其他局部中心和许多结构松散的行动者。CMOs的演化轨迹与 DAO 的虚拟性、弱中心、自主性等特征极度吻合,为 DAO 的诞生提供了网络参考模型。
At the Internet level, the spread of mobile Internet and mobile smart devices makes the virtual world an important space for people’s daily activities. CMOs are an online group of people who come together for a short period of time, guided by events or targets, to participate in, discuss and share certain social behaviour [10]. Human body searches [11-12], marines [13], crowdsourcing, etc. are typical of CMOs. Unlike the organized phenomena in nature, CMOs in virtual space are not limited by the physical world’s space, evolved by events or targets, rapidly formed, diffused and highly interactive processes, and automatically dismantled with the disappearance of targets. For example, the crowdsourcing phenomenon is a mission-driven local centre with clearly interactive structures and target orientations at a given time. As the mission is accomplished, the centre disappears and is replaced by other local centres and many loosely structured actors.
CMOs的理论模型进一步深化了 DAO 的实现基础。2004 年,王飞跃研究员提出了由人工社 会 (artificial societies ) 、计 算 实 验(computationalexperiments)和平行执行(parallel execution)组成的 ACP理论框架,为动态网民群体的计算建模和实验评估提供了系统化的研究思路和解决方案[15-16]。CMOs结合知识自动化[17]等手段,可以进行群体涌现行为计算与宏观社会现象预测,进而主动提供基于知识的智能推荐与基于决策的智慧服务,以此实现社会管理全过程的自动化实施[18],这也为 DAO 实现智能化管理提供了很好的借鉴。
The conceptual model of the CMOs further deepens the basis for the DAO realization. In 2004, the Wang Flying Fellows proposed the ACP theoretical framework, consisting of the Artificial Societies, Statistics, and parallel implementations, which provides systematic research ideas and solutions for the computational modelling and experimental assessment of dynamic web groups [15-16]. The CMOs, in conjunction with intellectual automation [17], provide a community-based approach to the prediction of phenomena associated with macro-social phenomena, and then offer knowledge-based intellectual advice and decision-based intellectual services as a way to automate the implementation of the whole process of social management[18], which also provides good lessons for DAOs to achieve intelligent management.
从人工智能的发展脉络来看,分布式人工智能不仅代表着未来的发展方向[19],同时也进一步为DAO的智能化管理提供了实现基础。分布式人工智能主要研究在逻辑或物理上分散的智能系统如何并行、相互协作地求解问题,在一个分布式系统中,既没有全局控制,也没有全局的数据存储,系统中的各路径和节点既能并发地完成信息处理,又能并行地求解问题,因此分布式人工智能系统比集中式系统更具开放性和灵活性[20]。此外,分布式人工智能系统并非一个封闭的系统,其可以与互联网、区块链等相连接,实现系统规模的指数级扩大。这样不仅提高了系统的灵活性、降低了问题的求解代价,同时也为智能化管理提供了实现手段。面向未来,DAO必然与人工智能相结合,从自动化走向智能化。未来 DAO中的每个个体都将是具备感知、推理、决策功能的智能代理(agent),能够部分或全部替代人类个体参与组织的运营、管理和决策,从而解决传统的委托—代理问题(principal–agent problem)[21]。
In the light of the development of artificial intelligence, distributed AI not only represents the future direction of development[19], but also provides a further foundation for the intellectual management of DAO. Distributed AI mainly examines how intellectual systems that are logically or physically dispersed can solve problems in parallel and in collaboration with each other. In a distributed system, there is neither global control nor global data storage, and the paths and nodes of the system are capable of completing information processing and solving problems in parallel, so that distributed AI systems are more open and flexible than centralized systems [20]. Moreover, distributed AI systems are not a closed system that can be connected to the Internet, block chains, etc., and expand the index level of system size. This not only enhances the flexibility of the system, reduces the cost of solving problems, but also provides the means for intelligent management. To the future, DAO must be combined with artificial intelligence and move from automation to intelligibility[20].
DAO理念的真正落地得益于区块链技术的出现[22]。区块链集成了分布式数据存储、点对点传输、共识机制、加密算法等技术,具有去中心化、去信任、不可篡改、集体维护等特点,可安全、高效地实现信息传输和价值转移[23-24]。此外,开源的有智能合约功能的公共区块链开发平台( 例如以太坊(Ethereum)),使得个体和组织可以借助区块链技术任意构建去中心化应用(decentralized application, DApp),组织的管理和运作规则便可能以智能合约的形式编码在区块链上,从而在没有第三方干预的情况下,依照预先设定的业务规则自主运营,实现分布式、自动化、自治型治理。2016 年,首个 DAO——The DAO 被开发出来,成为当时世界上最大的众筹项目。从此之后,一系列的 DAO 被相继推出,如Polkadot、Aragon DAO、DashDAO 等。然而,DAO 在实际落地的过程中仍面临一些问题,如安全性问题、法律问题、技术不成熟及智能化治理难题等。
In addition, open-source public sector network development platforms (e.g., Ethereum) have benefited from the emergence of block chain technology. Block chains have become distributed data storage, point-to-point transmission, consensus mechanisms, encryption algorithms, etc., with decentralised, untrustable, collective maintenance features that allow for secure and efficient information transmission and value transfer [23-24]. In addition, open-source public sector network development platforms with smart contract functions (e.g., Etheneum) have enabled individuals and organizations to develop decentralized applications (decentralized application, DApp) using block chain technology at their disposal, and the management and operation rules of the organization may be coded on the block chain in the form of smart contracts, thus operating autonomously without third-party intervention, according to pre-defined business rules, distributed, automated, autonomous governance. In 2016, the first DA-The DAO was developed as the largest crowd-building project in the world.
DAO 有望成为国家、市场、公司之外的第 4 种组织形态,最大化地实现组织的效能及价值流转,形成新的商业变革。然而,纵观学术界,以"分布式自治组织、分布式自治公司、去中心化自治组织"为主题词在谷歌学术及知网进行搜索,剔除不相关的文献后,与 DAO 相关的研究却寥寥无几。鉴于目前DAO 领域已呈现出明显的技术和产业创新驱动的发展态势,行业内却缺乏统一的界定和分析框架,本文致力于对其进行系统的分析与探讨。首先,对 DAO 的概念及特征做出界定;接着首次系统地提出 DAO 五层分析框架,并对每一层的构成要素进行详细介绍。在此基础上,对典型的 DAO 应用案例——Aragon 进行详尽剖析,之后概述 DAO 目前所面临的问题与挑战,并对其未来发展趋势进行展望,以期为未来的研究提供有益的启发与借鉴。
DAO is expected to become the fourth organizational form of the state, the market, and the company, maximizing organizational effectiveness and value flow, leading to new business changes. However, a systematic analysis and exploration of DAO concepts and characteristics has been undertaken throughout the academic community, using the theme "distributed self-governing organizations, distributed self-governing companies, decentralized self-governing organizations" as a theme term, followed by a first systematic search of the DAO five-tier analysis framework and detailed description of the composition of each layer. On this basis, the typical DAO application, Aragon, has been thoroughly analysed and outlined the problems and challenges currently faced by DAO and its future development trends have been developed, with a view to providing useful insights and lessons for future research.
2.1 DAO的概念
2.1 DAO concept
关于 DAO的界定,目前尚无统一的标准。DAO 作为加密技术革命的理想结果,最初源自 Ori Brafman在TheStarfishandtheSpider中提到的关于去中心化组织的主题[25]及 YochaiBenkler在 The WealthofNetworks提出的"同行生产"(peerproduction)[26]。随着加密数字货币的到来,2013年,Daniel Larimer 首次提出类似 DAO 的概念——去中心化自组织企业(decentralizedautonomous corporation,DAC),DAC 与传统企业的区别在于去中心化和分布式[22]。 2014 年 Daniel Larimer 再次补充了 DAC 的概念。随后,Vitalik 阐述了对 DAC的认识[27],并经由 Daniel Suarez 的 Daemon 一书启发,提出了区块链语境下的 DAO。而 DAO 概念首次正式提出则是在2015 年以太坊区块链上的一份名为 DAO 的智能合约中。此时的 DAO 是智能合约, 即技术框架、工具,常被理解为类似非盈利性组织的自组织。随着区块链技术的发展和应用,DAO 的定义更加多元化:数字货币、系统/机构,商业模式甚至是无人汽车平台都可称为DAO。
With the advent of the encrypted digital currency, Daniel Larimmer first proposed a concept similar to that of the DaO - decentralisation of organizational enterprises (decentralizedautonous technology, DAC), the difference between the DAC and traditional enterprises is that of decentralization and distribution [22]. Daniel Larimer in 2014 updated the DAC concept. Vitalik then described the DAC awareness [27] in 2013 and introduced the DAO-like concept, inspired by the Daniel Suarez model, into the regional DA language.
目前比较有代表性的概念是维基百科指出的:DAO 是一个以公开透明的计算机代码来体现的组织,它的金融交易记录和程序规则均保存在区块链上[28]。龚鸣指出,DAO 是一个完全自动运行的公司,任何人都可以随意地加入和退出,而股权(代币)成为系统中运行的唯一货币,让收入、利润等概念完全消失,随着组织生态的发展壮大,通过代币(股权)升值的方式让参与者获利[29]。
The current more representative concept is noted by Wikipedia: DAO is an organization represented by open and transparent computer codes, and its financial transactions records and rules of procedure are kept on the block[28]. Nina notes that DAO is a fully automated company that can be joined and withdrawn by anyone at will, while equity (indemonstration) becomes the only currency operating in the system, allowing the concepts of income, profit, etc. to disappear completely, benefiting the participants through the appreciation of the tokens (equity) as the organization grows.[29]
本文关于 DAO提出以下界定:DAO 是将组织不断迭代的管理和运作规则(共识)以智能合约的形式逐步编码在区块链上,从而在没有第三方干预的情况下,通过智能化管理手段和通证经济激励,使得组织按照预先设定的规则实现自运转、自治理、自演化,进而实现组织的最大效能和价值流转的组织形态。
The DAO is defined in this paper as a gradual codification of the rules of management and operation (consensus) of the organization in the block chain in the form of an intelligent contract, so that, without third-party intervention, the organization can operate on its own, self-governance, self-evolved in accordance with predefined rules and thus achieve the organization's maximum effectiveness and value flow organizational form.
(1)分布式与去中心化(distributedandde-centralized)
(1) Distributedandde-centralized
DAO 中不存在中心节点以及层级化的管理架构[30],它通过自下而上的网络节点之间的交互、竞争与协作来实现组织目标。因此,DAO 中节点与节点之间、节点与组织之间的业务往来不再由行政隶属关系所决定,而是遵循平等、自愿、互惠、互利的原则,由彼此的资源禀赋、互补优势和利益共赢所驱动。每个组织节点都将根据自己的资源优势和才能资质,在通证的激励机制的作用下有效协作,从而产生强大的协同效应。
There is no central node in the DAO and a hierarchical management structure [30], which achieves organizational goals through interaction, competition and collaboration between bottom-up network nodes. Thus, transactions between nodes and nodes, nodes and organizations in the DAO are no longer determined by administrative affiliation, but by the principles of equality, voluntariness, reciprocity, mutual benefit, and each organization’s resource endowment, complementarities, and co-benefits. Each node will be driven by a strong synergy, based on its resource advantages and merit, and will work effectively together under a certified incentive mechanism.
(2)自主性与自动化(autonomousandauto- mated)
(2) Autonomy and Automation (automousandauto-mated)
在一个理想状态的 DAO 中,管理是代码化、程序化且自动化的。"代码即法律"(code is law),组织不再是金字塔式而是分布式,权力不再是中心化而是去中心化,管理不再是科层制而是社区自治,组织运行不再需要公司而是由高度自治的社区所替代。此外,由于 DAO 运行在由利益相关者共同确定的运行标准和协作模式下,组织内部的共识和信任更易达成, 可以最大限度地降低组织的信任成本、沟通成本和交易成本。
In an ideal DAO, management is coded, programmed, and automated. The code is law, the organization is no longer pyramidal, but distributed, power is no longer centralized, management is no longer hierarchical, but community autonomy, and the organization no longer operates as a company, but is replaced by a highly autonomous community. Moreover, since DAO operations are more easily achieved within the organization, based on operating standards and collaborative models defined by the stakeholders, it minimizes the cost of trust, communication and transaction costs for the organization.
(3)组织化与有序性(organizedandordered)
(3) Organizing and Ordered
依赖于智能合约,DAO中的运转规则、参与者的职责权利以及奖惩机制等均公开透明。此外,通过一系列高效的自治原则,相关参与者的权益得到精准分化与降维,即给那些付出劳动、做出贡献、承担责任的个体匹配相应的权利和收益,以促进产业分工以及权利、责任、利益均等,使得组织运转更加协调、有序。
By relying on smart contracts, the rules of operation of the DAO, the rights of participants in their duties, and the mechanisms of rewards and sanctions are open and transparent. Moreover, through a series of efficient principles of self-government, the rights and interests of the participants concerned are precisely divided and reduced, i.e., by matching the rights and benefits of individuals who work, contribute, assume responsibilities in order to promote a division of labour and equality of rights, responsibilities, interests, etc.
(4)智能 化 与 通 证 化 (intelligence and tokenization)
(4)intelligence and generalisation
DAO底层以封装了支持DAO及其衍生应用的所有基础设施——互联网基础协议、区块链技术、人工智能、大数据、物联网等为技术支撑,以数字化、智能化、链上链下协同治理为治理手段,改变了传统的科层制以及人为式管理方式,实现了组织的智能化管理。通证(token)作为DAO 治理过程中的重要激励手段,将组织中的各个元素(例如人、组织、知识、事件、产品等)比特化、通证化,从而使得货币资本、人力资本以及其他要素资本充分融合,更好地激发组织的效能和实现价值流转。
Underpinning all infrastructure in support of DAO and its derived applications – Internet infrastructure protocols, block chain technology, artificial intelligence, big data, object networking, etc. – DAO bottom is technologically supported by digitalization, intelligence, coordinated governance under the chain as a means of governance, changing traditional hierarchies and man-made management, leading to intelligent management of the organization. Translator (token) serves as an important incentive in the DAO governance process, i.e., human, organizational, knowledge, events, products, etc., to better integrate monetary capital, human capital, and other factor capital, and to better stimulate organizational effectiveness and value flow.
鉴于业界对 DAO 仍缺乏统一的界定和分析框架,本节提出 DAO的五层架构参考模型,即基础技术层、治理运作层、激励机制层、组织形态层和表现形式层,如图 1 所示。
In view of the continuing lack of a coherent industry definition and analysis framework for DAO, this section proposes a five-tiered architecture reference model for DAO, i.e., the basic technical layer, the governance operating layer, the incentive layer, the organizational morphology layer and the expression layer, as shown in figure 1.
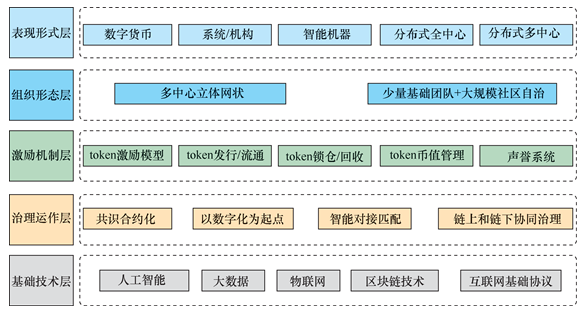

图1 DAO 的五层架构参考模型
Figure 1 Five-tier architecture reference model for DAO
3.1 以基础技术为底层基础设施层
基础技术层封装了支持 DAO及其衍生应用的所有基础设施,包括互联网基础协议、区块链技术、人工智能、大数据、物联网等。
The basic technology layer covers all the infrastructure supporting DAO and its derivative applications, including Internet base protocols, block chain technology, artificial intelligence, big data, object networking, etc.
(1)互联网基础协议
(1) Internet Basic Agreements
DAO 一般建立在对等式网络(peer-to-peer network,P2P)之上,以组织散布在全球的节点共同参与,因此互联网基础协议是 DAO 最底层的基础设施。
DAO is generally based on peer-to-peer network, P2P, to organize the participation of nodes scattered around the world, so the Internet base protocol is the lowest infrastructure of the DAO.
(2)区块链技术
(2) Block chain technology
DAO最显著的特点是去中心化与开放自治[31], 区块链是 DAO实现其功能特点的核心技术。区块链的共识机制使得决策权高度分散的去中心化系统中的各节点有效地就组织治理达成共识,从而解决传统科层制和金字塔式管理架构中存在的信息不对称、逆向选择等问题[32]。智能合约则将 DAO 的运营与管理规则以计算机代码的形式记录在区块链上,各方按照合约完成工作并依据贡献度进行利益分配,最终实现"代码即法律"式的智能化管理[33]。非对称加密、时间戳等技术用于保障 DAO 运行过程中的安全性需求和所有权验证。
DAO’s most notable feature is decentralisation and open autonomy[31], and the block chain is the core technology for the DAO’s functional characteristics. The block chain’s consensus mechanism allows the nodes of the decentralized decentralised system, where decision-making is highly decentralized, to effectively reach consensus on organizational governance, thereby addressing the information asymmetry, reverse selection and other problems that exist in traditional layers and pyramid-style management structures [32]. Smart contracts record DAO’s operating and management rules in the form of computer codes on the block chain, the parties’ work under contract and benefit allocation according to contribution, and ultimately achieve smart management of the code, i.e., the law. Asymmetric encryption, time stamping, etc., is used to safeguard the safety needs and ownership of DAO operations.
(3)人工智能
(3) Artificial intelligence
随着以深度学习、强化学习、生成式对抗网络(generativeadversarialnetworks,GAN)为代表的人工智能技术的快速发展,DAO中的每个个体节点都将成为自主和自治的智能体(软件代理或软件机器人),有望部分甚至全部取代人类实现推理、决策、协作等功能[34]。此外,智能合约也不再局限于按照预定义的"If-Then"式语句自动执行,还将具备未知场景下"What-If"式智能推演、计算实验以及自主决策等功能,使 DAO 真正成为集描述、预测、引导于一体的分布式自治组织。
With the rapid development of artificial intelligence technology represented by in-depth learning, intensive learning, and the generation of antagonistic networks (generativeadversarialworks, GAN), each individual node in the DAO will become an autonomous and autonomous intelligent body (software agent or software robot) with the potential to partially or even entirely replace human functions such as reasoning, decision-making, collaboration, etc. [34]. In addition, intelligent contracts are no longer limited to automatic implementation in the predefined "if-Then" language, but will also have the functions of "what-if" intellectual evolution, computational experiments and autonomous decision-making in the unknown setting, making DAO truly a distributed self-governing organization that describes, predicts, guides to one.
(4)大数据
(4) Big data
基于大数据及开源情报解析方法,可以实时采集运行在区块链系统中的 DAO 节点的状态数据、链内交易数据和系统运行数据,从而掌握并预测DAO 的演变规律与发展趋势。此外,区块链本身也是大数据安全、脱敏、合法、正确的保证。
On the basis of large data and open source intelligence resolution methods, data on the state of DAO nodes operating in block chain systems, intra-chain transactional data and system running data can be collected in real time to capture and predict the evolution patterns and trends of DAO. Moreover, the block chain itself is a guarantee of large data security, desensitization, legitimacy, and correctness.
(5)物联网
(5) Material networking
区块链可以与物联网技术相结合形成物联链(blockchain ofthings),从而对链下物理空间中的智能设备、实体资产等进行数字化改造并集成到区块链[35]中。作为可信物联网服务平台框架,DAO将以安全可信的方式监控智能设备的全生命周期,实现设备间的自主协作和交易,并利用智能合约实现智能化互操作。
Block chains can be digitized and integrated into blocks[35] of smart equipment, physical assets, etc., in the physical space under the chain, in combination with material networking technology. As a framework for a credible networking service platform, DAO will monitor the entire life cycle of smart equipment in a safe and credible manner, achieve autonomous collaboration and transactions between equipment, and use smart contracts for intelligent interoperability.
3.2 以智能化管理为主要治理手段
3.2 Smart management as the primary means of governance
DAO的治理是一种智能化自治,根据组织的性质和目标,将系列公开公正且获得共识的制度通过智能合约代码化,以数字化为起点、人工智能技术为保障、链上链下协同为治理手段,以及无边界的群体价值创造,实现组织的自治理和自演化。
DAO governance is an intelligent self-government that, in accordance with the nature and objectives of the organization, encodes a series of open, fair and consensual systems through smart contracts, digitalizes them as a starting point, artificial intelligence as a safeguard, synergies between the chains as a means of governance, and the creation of group values without borders, and achieves self-governance and self-evolvation of the organization.
(1)共识合约化
(1) Consensual contractualization
公司往往是在取得共识的契约的基础上获得业务或者实现良好的运转。建立合同的目的是依靠法律的约束力量对组织、个人的利益机制乃至社会的良性运转加以保障,但由于合同的履行不仅与当事人有关,还受外界环境的影响,因此合同履行本身有很大的不确定性。例如,合同效力难以判断、变更解除难以实现、违约难以追究,从而导致组织与组织、组织与个人之间信任程度下降,沟通成本增加。
Companies often get business or operate well on the basis of a consensual contract. The purpose of the contract is to rely on the binding force of the law to safeguard the functioning of the organization, the individual’s interests and society, but the performance of the contract itself is highly uncertain, as it is not only about the parties but also affected by the external environment. For example, contract effectiveness is difficult to judge, change is difficult to achieve, default is difficult to enforce, resulting in lower levels of trust between the organization and the organization, the organization and the individual, and increased communication costs.
DAO 以建立在区块链技术上的智能合约为信任基础。广义上的智能合约是一个无须中介、自我验证、自动执行合约条款的计算机交易协议[36],本质是将人、组织取得共识的法律协议以及网络之间的复杂关系程序化,利用协议和用户接口完成从协商到履行的所有步骤。DAO 通过多种属性的节点—— 代表性节点、专业人士以及技术人员等合约制定参与方之间的协商,明确各方的权利、责任、利益,
DAO is based on an intelligent contract based on block chain technology. A broad-based smart contract is a computer-trading agreement [36] that does not require mediation, self-certification, automatic enforcement of the terms of the contract. It is essentially a process of formalizing the legal agreement between people, organizations and complex relationships between networks, using protocols and user interfaces to complete all steps from consultation to implementation. DAO, through consultations among the participants in the contract-making process - representative nodes, professionals and technicians - defines the rights, responsibilities, interests of the parties.
确定共识性的标准合约文本,并将文本程序化和加以验证,从而获得标准合约代码,然后对代码化的合约进行分发、验证和自动执行。DAO 具备自动和强制执行合约条款的能力。
Determines the standard contract text of a consensual nature and processes and validates the text, thereby obtaining the standard contract code and then distributing, validating and automatically executing the coded contract. DAO has the ability to automatically and enforce the terms of the contract.
DAO 将共识/契约前置、信任锁定、法律嵌入, 解决了传统经济管理学中的"科斯定理—合约理论—产权理论—交易成本理论"的契约问题,极大地降低了记账(交易)成本,解决了信息不对称的问题,使得组织在治理及业务开展过程中从负和、零和博弈走向正和博弈。
DAO, by pre-empting consensus/contracts, locking in trust, embedding the law, solves the contractual problem of "Cos-contract theory-property theory-transaction cost theory" in traditional economic management, significantly reduces the cost of bookkeeping (transactional) and solves the information asymmetry that allows the organization to move from a negative, zero-sum game to a positive and competitive game in governance and operations.
(2)以数字化为起点
(2) Digitalization as a starting point
智能合约为 DAO治理提供信任保障,而DAO 治理的燃料剂在于数字化。DAO 治理以数字化为起点,贯穿始终。IT分为 3 个阶段,即老IT(工业技术)、旧 IT(信息技术)、新 IT(智能技术)。在传统的信息化时代,IT 重心停留在任务流、工作流、信息流模式,将人的工作环境和工作流程通过办公系统连接起来,实现业务和工作的协同。这个阶段一方面仍停留在典型的自上而下的科层管理体制上;另一方面,信息的加工处理仍依靠个人的专业知识进行,并未达到智能化。
Smart contracts provide trust guarantees for DAO governance, while the fuel agent for DAO governance is digitization. DAO governance starts with digitization and runs through it. IT is divided into three phases, namely, old IT (industrial technology), old IT (information technology), new IT (intelligent technology). In the traditional age of informatization, IT focuses on task flow, workflow, and information flow patterns, linking people's work environment and workflows through office systems to achieve business and work synergy. This phase remains on the one hand a typical top-down system of management; and, on the other hand, the processing of information is still dependent on individual expertise and does not achieve intelligence.
数字化的本质是收集数据、分析数据,并将数据应用于商业模式创新、商业生态重构、改善用户体验等,而数字化的基础是建立在信息技术、大数据技术以及互联网技术之上的。信息技术及大数据技术构成了数字化技术,具体包含数据收集、存取、建库、处理、分析、挖掘、模型预测和数据表达等环节。互联网技术作为桥梁,将人与机联合起来,不断"喂养"组织的数字化建设。
The essence of digitization is the collection of data, the analysis of data and their application to business model innovation, business eco-reconstruction, improved user experience, etc., while digitization is based on information technology, big data technology, and Internet technology. Information technology and big data technology constitute digital technologies that include, inter alia, data collection, access, build, process, analysis, excavation, model prediction, and data expression.
数字化不是目的,目的是通过数字化进行描述、预测、指导,为 DAO 打破边界及层级提供基础,同时为智能匹配、管理及决策提供参照物。另外,由数字化向"数字四胞胎"[37]发展是推动 DAO 智能化的基础。
Digitalization is not an end in itself. It is designed to describe, predict, guide, and provide the basis for DAO to break boundaries and hierarchies, while providing a reference for intelligent matching, management, and decision-making. Moreover, digitalization to "digital quadrends"[37] is the basis for promoting DAO intelligence.
(3)智能对接匹配
(3) Smart docking match
运行在去中心化处理和存储载体上的 DAO利用相关的 AI技术,将人、组织、知识、事件、产品或服务等元素任意组合进行匹配和对接,是 DAO降低沟通成本、提高效率以及实现规模化的核心。例如,对人/角色的智能匹配:通过数字化个体和组织的信息与行为数据,根据贡献及能力匹配个体 DAO所处的位置或承担的角色。对事件的智能匹配:通过节点画像,自动实现任务识别、推荐、匹配和对接,从而解决信息孤岛问题,快速调动组织人力和知识资本。对知识的匹配:根据节点信息及行为数据(如点击、搜索、浏览)进行匹配、推荐,知识推荐是目前较为成熟的一种技术。智能评价/考核:对个体完成任务的过程、结果进行多维度评价,评价结果代表该个体在 DAO 荣誉体系中所属的层级,不同层级享有不同的权益。
Runs DAO on decentralised processing and storage vehicles, using the relevant AI technology, to match and dock elements such as people, organizations, knowledge, events, products or services at random, and is at the core of DAO's efforts to reduce communication costs, improve efficiency and scale. For example, smart matching of people/roles: to match individuals'positions or roles with contributions and capabilities. Smart matching of events: to automatically achieve mission identification, recommendation, match and match-up, and to quickly mobilize organizational human and intellectual capital through node imageing. Matching knowledge: to match, recommend, and recommend knowledge based on node information and behavioural data (e.g., clicks, searches, browsing), is a more mature technology. Smart evaluation/testing: multi-dimensional evaluation of the individual's process and results, which represents the individual's hierarchy in the DAO honor system, with different levels of interest.
另外,AI 效力建立在有效数据模型的基础之上,即"喂"大量数据训练其智能,但数据孤岛及隐私安全问题严重制约了 AI 的发展。DAO 本质上鼓励共享,尤其是在没有单一实体的控制下,能打破中心化数据孤岛,为AI 精准推荐、匹配提供数据。
Moreover, AI’s effectiveness is based on an effective data model, that is, “feeding” a lot of data to train its intelligence, but data silos and privacy security issues seriously constrain AI’s development. DAO essentially encourages sharing, especially in the absence of a single entity, to break down central data silos and provide data for AI’s precision recommendation, matching.
(4)链上和链下协同治理
(4) Synergy governance on and below the chain
与传统组织管理模式不同的是,DAO 通过链上和链下协同治理的方式改变了以往少数控股股东利益或债权人利益至上的中心化管理模式。
In contrast to the traditional organizational management model, DAO has changed the previous model of centralized management of the interests of a minority of controlling shareholders or the interests of creditors through coordinated governance on and below the chain.
链上治理是将共识机制以智能合约的方式加以确定、更新和维护,本质是在互不信任的环境中创造一个可信的系统,保证利益相关者的权益。共识机制是互不信任的节点通过遵循预设机制最终达到数据的一致性,即由多方参与寻求相对平衡的利益共享机制,改变以往的公司治理模式。共识机制主要包括实用拜占庭容错(PBFT)、授权拜占庭容错(DBFT)、工作量证明(POW)、权益证明(POS)、股份授权证明(DPOS)以及其他混合共识算法[38]。链下治理是为了保证共识机制的确立、认可、扩散以及更新所采取的一系列治理手段的协同治理方式。与其他非盈利性组织的治理结构类似,大多数采用"基金会+受委托公司+表现形式"的治理结构。
The consensus mechanism is the ultimate consistency of data by following predefined mechanisms, i.e., by involving multiple parties in the search for a relatively balanced benefit-sharing mechanism, changing the previous corporate governance model. The consensus mechanism consists mainly of practical Byzantine error (PBFT), delegation of authority to Byzantine error (DBFT), workload certification (POW), proof of equity (POS), share authorization (DPOS) and other mixed consensus algorithms. Governance under the chain is about ensuring that consensus mechanisms are established, recognized, diffused, and updated in a coordinated manner with a range of governance tools.
由于当前技术的限制,DAO 治理更多地采用"小部分链上治理+主要的链下治理"的模式,随着技术的成熟,正逐步向链上治理转移。另外,分叉是解决 DAO 治理僵局的有效手段,分叉包括软分叉和硬分叉(如果分叉后新生成的区块可以被原先的矿工所接纳,则称为软分叉;否则为硬分叉)。分叉相比传统上市公司的治理分歧造成的市场冲击较低,也体现了基于共识机制的利益相关者治理模式的优势。
Due to current technological constraints, DAO governance is increasingly based on the model of "Governance on a small segment of the chain plus Governance on the main chain" and is gradually shifting to governance on the chain as the technology matures. Moreover, the fork is an effective means of resolving the DAO governance impasse, including soft fork and hard fork (which is known as soft fork if the newly created blocks can be accepted by the original miners; otherwise, hard fork). The fork is lower than the market fork than the traditional differences in governance of municipal companies and reflects the advantages of a consensus-based governance model for stakeholders.
3.3 以基于区块链的通证经济为主要激励手段
3.3 The hyphenic economy based on block chains is the main incentive
通证是一种可流通的数字资产和权益证明[39-40], 现实世界中的股票、债券、期权、积分等均可以通证的形式实现数字化。一般认为,通证至少集股权属性(可增值、具有长期收益)、物权属性(代表使用权、商品或服务)和货币属性(在一定范围内可流通)于一体。
Passors are negotiable digital assets and certificates of interest [39-40], and stocks, bonds, options, credits, etc. in the real world can be digitized in the form of hyphens.
DAO 的发起者、开发者以及其他利益相关者等以共享形式拥有系统产权,而其他参与主体的主要经济激励则为基于区块链的通证。由通证创造的全新经济模型称为通证经济[41],具体是指借助通证这一加密数字资产的金融属性,对商品及服务进行通证化映射,让其在区块链上实现低成本甚至零成本的交易和切割。目前常见的通证类型包括支付型通证、功能型通证以及资产型通证。通证经济是行为管理和激励工具的系统方法,区块链与通证的结合可以实现不同价值系统间的"价值转换"与"价值转移"[42]。
The initiators, developers, and other stakeholders of DAO, among others, have ownership of the system in a shared form, while the main economic incentives of the other participating entities are hyphens based on block chains. The brand-new economic model created by hyphenation is called hyphenics.[41], specifically, a hyphenized mapping of goods and services to enable low- or even zero-cost transactions and cuttings on the block chain. Current common hyphens include payment-type hyphens, functional hyphens, and asset-type hyphens. The hyphenics economy is a systematic method of behavioural management and incentive tools, and a combination of block chains and hyphens can achieve "value conversion" and "value transfer" between different value systems[42].
每个 DAO 都可以发行通证,并且通常可以根据项目属性,对通证的发行量、流通量、锁仓期、分配方式等通证模型的相关要素进行设置[43]。通证模型设计本质上是机制设计问题,目标是促进参与主体的激励相容,实现共赢。良好的通证模型一方面能将货币资本、人力资本以及其他要素资本融合起来,改变人与组织的关联关系,降低组织运行成本,同时服务于项目早期的资金需求;另一方面,由于通证锚定的是项目本身,优质项目使得通证的市场价值不断提升,并能够更好地对参与主体形成激励。
Each DAO can issue a pass, and usually sets up the relevant elements of a pass model based on project attributes, such as issue, circulation, lock-down and distribution patterns. The pass model design is essentially a mechanism design issue with the objective of promoting incentives for participating subjects to be compatible and win-win. A good pass model can, on the one hand, combine monetary, human and other factor capital, change human-organizational connections, reduce organizational operating costs and serve the early financial needs of the project; and, on the other hand, because the licence anchors the project itself, quality projects increase the market value of the pass and are better able to create incentives for participating subjects.
3.4 以混序立体为主要的组织形态
3.4 The main organizational form is the mix 3D
组织形态作为历史的产物,与所处时代的经济、文化、环境有很大的关系。随着技术的发展和经济社会的进步,组织在演进的过程中摒弃了传统的单线竞争和线性思维,不再局限于内部以及科层的管理体制,并打破了价值活动分离的机械模式。
As a product of history, organizational patterns have a great deal to do with the economy, culture, and environment of the time. With technological advances and economic and social progress, the organization has moved away from traditional single-line competition and linear thinking, from being confined to internal and scientific management systems, and from breaking down mechanical patterns of separation of value activities.
基于价值网络的 DAO是一个混序、扁平、平行(虚拟与现实)、人机合一的多中心的生态立体网状组织结构,它打破了基于分工的功能式组织结构,实现了从垂直协同到平行协同、从井然有序到混序、从追求稳固和固化到追求相对稳定和动态平衡、从相对单一的形态到多样化的形态的转变,具体表现如下。
The value network-based DAO is a mixed, flat, parallel (virtual and realistic) multi-centre eco-crete networked organizational structure that breaks down a functional organizational structure based on division of labour and brings about a shift from vertical to parallel synergies, from vertical to stratification to mixing, from the pursuit of solidity and solidification to the pursuit of relative stability and dynamic balance, from a relatively single form to a diversified form, as shown below.
① 扁平:打破组织上下层级。人和人之间、人和组织之间的关系被重新定义,既能充分发挥独立个体的灵活性,又能实现透明垂直管理的高效性。
1 flat: Breaking down the top and bottom of the organization. Relationships between people, people, and organizations are redefined so that the flexibility of independent individuals can be fully realized and the efficiency of transparent vertical management can be achieved.
② 开放:打破组织内外边界。DAO 根据特定项目、需求和任务随时调整,又可随着任务的完成而自行裂变、解散、消亡。
Open: Breaking the internal and external boundaries of the organization.
③ 平行:在现实中的人和组织之外建立一个与之平行的虚拟人和组织,通过两者的虚实交互、闭环反馈以及链上链下协同治理,实现组织治理的决策寻优与平行调谐[44]。
3 Parallel: Create a parallel virtual person and organization outside the reality of people and organizations to achieve excellence in organizational governance and parallel harmonization of decision-making through virtual interaction between the two, closed-ring feedback and synergetic governance in the chain[44].
④ 人机合一:随着技术的进步,未来的 DAO 将进一步演变为人机合一。DAO中的智能代理/软件机器人将会在得到授权后替代人类开展业务活动并在彼此间开展竞争博弈和协调合作。
4 Humans: As technology advances, future DAOs will evolve further into humans. Smart agents/software robots in DAOs will replace humans when authorized to operate and to compete and coordinate with each other.
3.5 多样化的表现形式
DAO的表现形式多样,根据所提供的服务,它既可以是数字货币,也可以是一种系统或者机构(如应用平台以太坊),甚至可以是互联的智能机器(如无人驾驶)。根据组织的控制力,DAO既可以是分布式全中心化(如公链形态),也可以是多中心(如联盟链形态)。每个 DAO都有其特有的共识和协议,每个节点都有权查看所拥有的代币,并获得相应的股息,但 DAO仍需依靠现有的法律框架展开业务活动。因此,在法律结构实体上通常借鉴"非盈利性基金会+受委托公司+表现"的形式(如开源社区),具体为"由基金会作为通证发行主体进行资金的募集、分配、管理以及监督等,同时委托部分公司进行技术开发、市场推广和运营、基金投资和管理以及其他法律服务"。然后,以开源社区或其他组织的模式呈现,推动 DAO 展开链上、链下的协同治理。除此之外,部分组织还会使用离岸实体控股基金会。DAO 法律结构实体如图 2 所示。
Each DAO has its own consensus and agreement that each node has the right to see its currency and to receive the corresponding dividends, but the DAO still needs to rely on the existing legal framework for its operations. Thus, the form of "non-profit foundations plus the performance of entrusted companies" (e.g., open communities) is usually used in legal entities, specifically for "fund collection, allocation, management and supervision by the Foundation as a public issuer" (e.g., public chain form). In addition, a number of companies are entrusted with technological development, market promotion and operation, investment and management and other legal services.
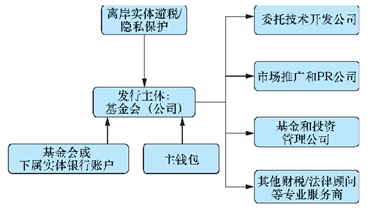

图 2 DAO 法律结构实体
Figure 2 DAO Legal Structured Entities
目前业界关于 DAO 的应用较多,但具代表性的案例较少,典型的如The DAO、Steemit、Digix DAO、Aragon 等。下面以第 3 节提出的五层架构模型为基础,选取 Aragon 案例进行详细分析。
There are currently more applications of DAO in industry, but there are fewer representative cases, typically The DAO, Steemmit, Digix DAO, Aragon, etc. The five-tier architecture model presented in section 3 is the basis for a detailed analysis of the Aragon case.
4.1 Aragon
Aragon是一个方便用户创建和管理各类 DAO(公司、非盈利性组织、开源项目)的 DApp,使用户可以跨越国界自由地创建无等级制度、依赖彼此协作自运行的组织。每个 DAO 基于系列智能合约存在,智能合约规定了组织的股东构成及相应的权利、义务。建立在 Aragon上的智能合约系统被称为 AragonOS 。AragonOS 保证只有授权的账户及合约(统一被称为实体,entities)拥有实施特定行为的权利。每个 AragonDAO 拥有若干个App,基本的 App包括通证管理、投票以及金融。除此之外,任意一个个体都可以开发自己的 App 并将其添加至他们所在的 DAO中,这些 App 拓展了组织的功能,具体如图 3 所示。
Aragon is a user-friendly DAP for creating and managing various types of DAO (companies, not-for-profit organizations, open-source projects), allowing users to freely create non-hierarchical organizations across national borders, relying on one another to operate on one another. Each DAO is based on a series of smart contracts, which define the organization’s shareholder composition and corresponding rights and obligations. The smart contract system built on Aragon is known as AragonOS. AragonOS guarantees the right to perform certain acts only on authorized accounts and contracts (collectively known as entities, entities). Each AragonDAO has several Apps, the basic App includes pass management, voting, and finance. In addition, any individual can develop his or her App and add it to their DAO, which expands the organization’s functions, as shown in Figure 3.
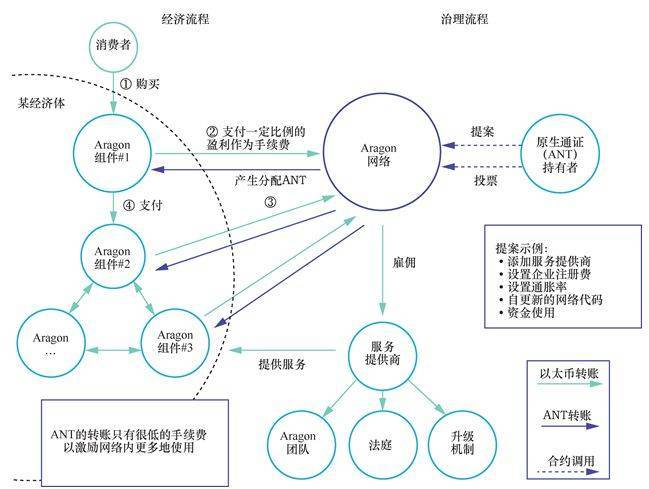

图3 Aragon流程
Figure 3 Aragon process
4.2 AragonDAO框架分析
4.2 AragonDAO framework analysis
根据第 3 节提出的 DAO 五层架构模型,对Aragon 的相关要素分析如下。
Based on the DAO five-storey architecture model presented in section 3, the relevant elements of Aragon are analysed below.
(1)基础技术
(1) Basic technologies
首先,Aragon基于以太坊建立,以太坊是一个永不宕机的全球公有区块链平台。其次,通过Aragon Core 进行搭建,AragonCore 是由 Solidity 语言的 DAO 和 DApp 组成的。Aragon 目前实现了股东名册、代币转账、投票、职位任命、融资、会计等组织机构的基础功能。Aragon链上组织的行为可以通过修改章程来自定义。最后,Aragon 组织可通过连接智能合约的第三方模块进行扩展。
First, Aragon built on Ether, a never-ending global public block chain platform. Second, built through Aragon Core, the AragonCore is composed of Dao and Dapp in the language of Solidity.
(2)治理运作
(2) Governance operations
Aragon 是流动的、民主的,通过 Aragon网络治理。Aragon 网络是该平台中的第一个 DAO,其目标是充当数字司法权。它首先从一个经投票通过的简单的宪法启动,当需要补充新的治理机制时,经提案和投票审核通过部署在链上。这个机制使得Aragon 可通过提案来升级治理机制,具体过程如下。
Aragon is mobile and democratic, governed through the Aragon network. The Aragon network is the first DAO in the platform to act as digital justice. It starts with a simple constitution that has been voted out, and when new governance mechanisms need to be supplemented, it is approved and deployed on the chain with proposals. This mechanism allows Aragon to upgrade governance through proposals, as follows.
首先,Aragon 拥有 Aragon 治理提案(Aragon governance proposal,AGP),每个 AGP 都详细描述了对 Aragon 网络共享资源进行管理、分配以及使用所要做出的改变。所有的 AGP 必须与社区的目标和价值相一致。AGP的目的是对 Aragon 网络共享资源的改变提供一个结构化的决策流程。对于共享资源的调整,需要 DAO 参与者共同决定同意/ 拒绝访问,或者批准/拒绝有关提案。
First, Aragon owns the Aragon governance proposal (Aragon government proposal, AGP), and each AGP details the changes that will be made to manage, allocate and use the shared resources of the Aragon network. All AGPs must be consistent with the goals and values of the community. The AGP aims to provide a structured decision-making process for changes in the shared resources of the Aragon network. For resource-sharing adjustments, DAO participants are required to agree/reject access or approve/reject proposals.
其次,AragonDAO可以指定哪些地址可以代表组织实施特定的行为,这是通过一个访问控制清单(accesscontrol list,ACL)来实现的。清单上的地址可以是外部账户,也可以是合约账户。通过将多个智能合约集合在一起,可以定义限制组织内部相关行为的复杂准则。例如,如果一个 DAO 想调动一笔资金,则必须满足:① 由组织内部的一位成员所提议;② 被绝大多数的成员所批准;③ 在一个预算范围之内。如图 4 所示。
Second, AragonDAO can specify which address can be used to carry out a particular act on behalf of the organization, which is done through an access control list (access control list, ACL). The address on the list can be either an external account or a contractual account. By bringing together multiple smart contracts, it can define complex criteria that limit related behaviour within the organization. If, for example, a DAO wishes to mobilize a fund, it must satisfy: 1 proposed by a member within the organization; 2 approved by an overwhelming majority of members; 3 within a budget, as shown in figure 4.


图4 Aragon DAO决策流程
Figure 4 Aragon DAO decision-making process
最后,当有争端发生时,Aragon 具备一个法庭协议(court protocol)来提供争端解决服务。具体来说,当一起争端发生时,一个陪审团被组建出来(组织成员可以通过预存一笔押金的方式成为一名陪审员,并在争端解决后获得一笔酬金),陪审员们需要就有关争议在一定的期限内提交一份裁决,最终的裁决结果依据绝大多数陪审员的意见而定。如图5 所示。
Finally, when a dispute arises, Aragon has a court agreement (court protocol) to provide dispute resolution services. Specifically, when a dispute arises, a jury is formed (the members of the organization can become a jury by depositing a deposit and receiving a fee after the dispute has been settled), the jurors are required to submit a decision on the dispute within a certain period of time, and the final decision is based on the opinion of the majority of the jurors.
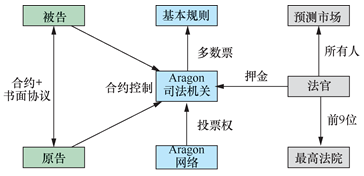

图5 Aragon DAO仲裁流程
Figure 5 Aragon DAO arbitration process
(3)激励机制
(3) Incentives
Aragon 网络上的原生通证被称为 Aragon net- work token(简称为 ANT)。ANT 代表用户在其所在 DAO 中的通证份额大小。DAO 中的成员可以就组织的规则和治理发起提案,之后其他成员根据自身所持有的通证份额大小进行投票,以决定是否接纳该提案。需要指出的是,提案的发起者也需要预存一定的 ANT 作为抵押,以促使提案者发起有益提案。
The original generality on the Aragon network is called Aragon net-work token. ANT represents the user’s share of the pass in its DAO. Members in the DAO can initiate a proposal on the rules and governance of the organization, followed by a vote by other members on the basis of their share of the pass to decide whether or not to accept the proposal.
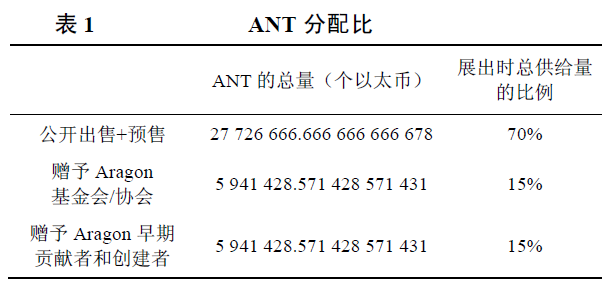
ANT 最初以公开代币出售的方式进行创造和分发,早期共有价值为275 000个以太币的 ANT 出售。如果加上预售时卖出的ANT、赠予Aragon 基金会/协会的ANT,以及赠予Aragon 创建者和早期贡献者的ANT, ANT 的初始总供给量为39 609523.809 523 809 54个以太币。分配比例见表 1。
ANT was originally created and distributed in the form of public currency sales, with an early total value of 275,000 ANTs sold in TTs. If ANTs sold in pre-sales, ANTs given to Aragon Foundations/Associations, and ANTs given to Aragon founders and early contributors, the initial total supply of ANTs was 39,609523.809,523,809,54 in TTs.
另外,Aragon DAO 采用声誉系统,所有的业务合作都可以互相评分,如组织可以评判承包商,同时承包商也可以评判该公司。所有评判关系的审计痕迹可以被追溯其真实性,进一步激励 Aragon DAOs。声誉值在 Aragon 网络中非常有价值。
Moreover, Aragon DAO uses a reputation system that allows all business cooperation to be rated against each other, such as the organization’s ability to judge the contractor and the contractor’s ability to judge the company. The audit trail of all the relationships can be traced back to its authenticity, further stimulating Aragon DAOs. The reputation value is very valuable in the Aragon network.

(4)组织形态
(4) Form of organization
Aragon 网络为用户创造和管理 DAO 提供基础设施和服务(例如 AragonOS)。Aragon 去中心化程度比较高,一方面 Aragon创始人并没有保留董事会的职位,而是由 AragonOne 负责技术开发, Aragon Black负责运营,Aragon Forum 负责讨论和监督,Aragon 协会负责整个项目的财政,并由社区代表就任;另一方面,用户可以自主定义所创建的DAO 的目的、类型、激励措施。DAO 去中心化的程度由创建者自己决定。截至 2019 年 7 月 9 日, Aragon 平台所创建的 DAO 的数量为 604 个。随着技术的成熟,Aragon 亦会逐步将项目的控制权移交给用户,从而实现自身治理的去中心化。Aragon 网络的最终目标是自身也发展成为自治组织,由希望社区繁荣的成员来共同维护。因此,就目前而言,Aragon 处于"少量基础团队+大规模社区自治"的阶段。
The Aragon network provides infrastructure and services for users to create and manage DAO (e.g. Aragonos). The Aragon network provides infrastructure and services for users (e.g. Aragonos). The extent to which the DAO is centralized is determined by the creators themselves. As of July 9, 2019, the number of DAOs created by the Aragon platform is 604. As technology matures, Aragon will gradually transfer control of the project to the users, with a view to centralizing its own governance. The ultimate goal of the Aragon network is to develop itself as self-governing organizations and to be jointly maintained by members of the community who want to prosper.
(5)表现形式
(5) Expressions
目前 Aragon 表现为公共开发平台,它使任何人都能创建和管理任意组织(公司、开源项目、非政府组织、基金会、对冲基金等)的 DApp。
At present, Aragon is a public development platform that enables anyone to create and manage Dapps for any organization (companies, open source projects, non-governmental organizations, foundations, hedge funds, etc.).
4.3 小结
4.3 Summing up
五层架构模型并不代表每个 DAO系统都要包含所有的元素,而是具备五层架构。Aragon DAO 是业界典型的 DAO应用平台,旨在解决 DAO 中以人为本的治理问题。对 AragonDAO 进行分析可知,底层基础架构以开源的具有智能合约功能的公共区块链平台以太坊为基础,通过 AragonCore 和功能化模块自由组合 DAO。在治理运作层,Aragon属于典型的链上治理,投票、提案、启动宪法、仲裁等行为均在 Aragon 网络上完成。不过 Aragon 的链上治理普遍面临选民投票率不足的问题,而且在一些关键决策上社区易产生分歧(例如 AGP42 提案——是否应该专注于以太坊/以太坊与 Polkdot 的选择)。就激励层而言,ANT 是 Aragon 的唯一代币, Aragon网络上节点的所有行为(如提案、投票、仲裁、交易等)均以 ANT 为交换媒介,将人力资本、货币资本和其他资本要素很好地结合起来;而 ANT 的分配由社区决定,极大地调动了社会节点的共建积极性。组织形态上,Aragon采用了典型的"少量基础团队+大规模社区自治"的模式,比如 Aragon 由平台的一个子系统(或称为 DApp)维持系统的基础运转。表现形式上,Aragon 表现为一个公共开放平台, Aragon DAOs 可以呈现为任意形式。
The five-storey architecture model does not mean that each DAO system contains all the elements, but has five layers of architecture. Aragon DAO is a typical DAO application platform for people-centred governance in the industry, which aims to address the issues of people-centred governance in the DAO. AnagonDAO is analysed, and the bottom base structure is based on open-source public block platforms with smart contract functions (e.g. AGP42 proposal - whether to focus on the choice of a remote/top-based module with Polkdot. At the governance operating level, the Aragon is the typical chain of governance, and the actions of the Aragon team are accomplished on the Aragon network.
DAO现在尚处于起步阶段,在对以往的组织形态、商业模式、管理方式进行迭代升级的同时,也面临诸多挑战。现阶段,从理论研究和现实应用的角度来看,DAO 还存在一些问题,距离大规模的应用还有较长的路程。
DAO is still in its infancy and faces many challenges as it upgrades past organizational patterns, business models, and management practices. At this stage, there are still problems with DAO from the point of view of theoretical research and practical application, and there is still a long way to go from large-scale applications.
5.1 理论研究
DAO理论研究尚处于起步阶段。虽然自组织理论群、ACP 理论框架、多中心治理(polycentric governance)理论以及自主治理理论(self-governance theory)[45]等研究为 DAO 的落地提供了理论指导, 但与 DAO 直接相关的研究寥寥无几。DAO 是对建立在传统组织架构基础之上的组织的再次升级和变革,对组织的技术支撑、治理机制、激励模式提出了新的要求。人们期望能够在组织系统的设计中更多地采用自治思想,但真正面向 DAO 系统设计的理论基础和模型验证等方面的研究非常少。基础理论的研究对于 DAO 的设计非常重要,将为 DAO 的实践以及工具的研究提供理论基础。
While studies such as those that have provided theoretical guidance to DAO landings since organizing the theoretical cluster, ACP theoretical framework, multi-centre governance theory, and self-government theory[45], there are few studies directly related to DAOs. DAOs are new demands on organizational technical support, governance mechanisms, and incentive models. There are expectations that there will be greater use of autonomy in the design of organizational systems, but very few studies on the theoretical underpinnings and model validation of DAO systems.
5.2 现实应用
5.2 Practical application
(1)安全问题DAO 建立在区块链、智能合约、人工智能等基础技术之上,由于这些技术本身不成熟以及存在安全隐患,DAO 目前也面临着较为严重的安全性问题。以智能合约为例,2016 年,当时世界上最大的众筹项目、同时也是第一个建立在以太坊区块链上的 DAO——The DAO 上链不久便遭到黑客攻击, 黑客利用智能合约代码中的可重入性漏洞(reentrancy vulnerability)发动了攻击,造成了超过 5000 万美元的以太币被盗,最后社区不得不以硬分叉的方式追回了资金。但此举违背了"代码即法律"的准则,引发了巨大争议。其他已知的智能合约安全性问题还包括交易顺序依赖(transactionorderingdependence, TOD)、时间戳依赖(timestampdependence)、处理异常(mishandled exceptions)等[46-47],它们极大地制约了 DAO的发展,亟待解决。
(1) Security DAO is based on basic technologies such as block chains, smart contracts, artificial intelligence, which, because of their own immaturity and security risks, are currently facing more serious security problems. In the case of smart contracts, 2016, the world's largest crowd-raising project, the first of which was built on the chain of the Tetha Zone, was attacked shortly by hackers, who took advantage of rematchable gaps in the smart contract code, resulting in over US$ 50 million being stolen in coins, and the final community had to recover money in a hard-fork manner. This, however, was contrary to the "code is the law" rule, causing huge controversy. Other known security issues in smart contracts include sequential dependence on transactions, TOD, temporal dependence, management of anomalies, etc. [46-47], which significantly constrains the development of DAO.
(2)技术局限性
(2) Technical limitations
DAO 虽向往"代码即法律"式的代码化治理, 但在实际操作中却很难实现。这是因为传统纸质合约中的法律条款(也称湿代码,wet code)和 DAO 智能合约中写入的规则(也称干代码,dry code) 之间存在巨大的语义鸿沟:前者为实现更高的通用性,通常使用简约、包容、灵活的自然语言在高度抽象层次上起草;而后者作为语义明确的代码,须使用严格且形式化的语言对规则进行精确描述。翻译过程中难免会引入误差[48],而且很多情况(比如某些边缘案例)是很难甚至无法编程的,这在一定程度上制约了 DAO 的应用和普及。
DAO, while moving towards "code or law" coding, is difficult to achieve in practice. This is because there is a huge semantic gap between the legal provisions in traditional paper contracts (also known as wet code, wet code) and the rules written in DAO smart contracts (also known as dry code, dry code), which are usually drafted at a high abstract level using simple, inclusive and flexible natural languages, and, as semantic codes, require a precise description of the rules in strict and formal language. The translation process will inevitably introduce errors [48] and many situations (e.g., some marginal cases) are difficult or even impossible to programme, which in part limits the application and universalization of DAO.
(3)法律问题
(3) Legal issues
由于 DAO具有去中心化、跨国界、成员匿名化等特征,一旦实际运营过程中出现法律问题,将会导致难以追责以及缺乏事后救济等问题。此外,当前DAO在法律层面尚未有明确的界定,有观点认为DAO是单纯的伙伴关系或合资企业,也有观点认为DAO更像是投资合约或证券的翻版。因此,未来《中华人民共和国公司法》《中华人民共和国合同法》《中华人民共和国证券法》《民商法》等法律条文需对DAO做出界定,以便明确使用法律的范围,使 DAO 承担相应的责任并履行相关的义务。
Moreover, there is currently no clear legal definition of DAO as a mere partnership or joint venture, or as a replacement of investment contracts or securities. Therefore, legal provisions such as the People’s Republic of China Contracts Law of the People’s Republic of China and the Securities Law of the People’s Republic of China need to define DAO so that the scope of the law can be clearly defined and DAO can be held liable and obligated.
(4)智能化治理难题
(4) Smart governance dilemmas
DAO的自运转很大程度上取决于组织内外所达成的共识程度及智能化管理手段。共识的确立、稳固、扩大、迭代以及协作流程的模块化、流程化等都是需要在前期构建的,而此阶段DAO 相对于中心化组织效率较低,支持 DAO 及其衍生应用的基础设施不成熟,使得组织前期很可能处于一种低效、混序的状态。另外,由于不同DAO 治理模式的差异化,现有的记账工具并不能满足DAO 的个性化需求,大多数小型的 DAO 前期记账只能采取手工的方式进行。但利益的明确划分意识较为薄弱,以至于DAO 在快速发展的过程中,由于前期核心建设者的利益未取得共识造成去中心化自治组织治理难的也不在少数。
The self-functioning of DAO depends to a large extent on the degree of consensus reached within and outside the organization and the means of intelligent management. Consensus-building, solidity, expansion, iterativeization, modularization of collaborative processes, etc., all need to be built in front of the stage, where DAO is less efficient than a centralised organization, and the immature of the infrastructure supporting DAO and its derivative applications, making the organization likely to be in an inefficient, mixed state.
为解决以上问题以及为 DAO 大规模应用打下基础,未来应从以下几个方面对DAO 做进一步的研究。
In order to address these problems and to lay the groundwork for the large-scale application of DAO, further research on DAO should be undertaken in the future in the following areas.
① 加强理论研究。首先,对 DAO 组织的概念及特点进行界定,对DAO 的清晰界定有助于对DAO 的理论研究。其次,理论基础可以借鉴经济学、生物学、人类社会、公共管理等从宏观和微观两方面对 DAO 的性质和机制进行研究,为 DAO 的设计和验证打下基础。
1 To strengthen theoretical research. First, to define the concepts and characteristics of DAO organizations, a clear definition of DAO contributes to the theoretical study of DAOs. Second, the theoretical basis can be drawn from macro- and micro-level studies of the nature and mechanisms of DAOs, drawing on economics, biology, human society, public administration, etc., to lay the foundation for the design and validation of DAOs.
② 在安全问题方面,智能合约的正式验证[49]和多方安全审计,智能合约条款转换标准的制定和监管沙盒是提高 DAO安全和隐私保护的有效途径。在法律问题方面,针对目前缺乏相应的法律、法规[50]的现状, 加强对法律层面DAO的责任以及法律适用中的问题和管辖权的立法,从而确认 DAO的权利、义务和责任。
In the area of security, formal certification of smart contracts [49] and multiple security audits, the establishment of standards for the conversion of smart contract terms and the regulation of sandboxes are effective ways to improve the security and privacy protection of DAO. In the area of legal issues, and in the light of the current lack of corresponding laws, regulations [50], strengthen legislation on the liability of DAOs at the legal level, as well as issues and jurisdictions in the application of the law, thereby recognizing the rights, duties and responsibilities of DAOs.
③ DAO与平行区块链结合,解决智能化治理难题。DAO 可视为一个由大规模智能体节点通过社会网络连接组成的社会系统, 具有不确定性(uncertainty)、多样性(diversity) 和复杂性(complexity)(即 UDC)。为了实现对 DAO的有效管理与控制,可以采用平行区块链的方法[51]。平行区块链是 ACP[52]方法与区块链技术的有机结合。平行区块链将促使 DAO从 UDC 系统转化为一个针对具体场景和任务的,兼具灵捷(agility)、聚焦(focus)和收敛(convergence)(即 AFC)特征的智能社会系统。DAO还可借鉴 ACP在平行装卸系统中的描述智能、预测智能和引导智能功能[53], 推动 DAO的平行智能[54]。此外,还要考虑将既有的公司制与 DAO的优势相结合,不仅仅是为了去中心化而去中心化,而是从更多的维度出发,在多变的环境中实现更好的协作,从而实现组织效用的最大化,并在此基础上最终实现去中心化自治社会(decentralized autonomous society,DAS)。
3 DAO combines with parallel block chains to solve problems of intelligent governance. DAO can be seen as a social system with large-scale smart body nodes connected through social networks, with uncertainty (uncertability), diversity and complexity (i.e. UDC). In order to achieve effective management and control of DAO, parallel block chains [51] can be used. Parallel block chains are the organic combination of ACP [52] methods and block chain technologies. Parallel block chains will facilitate the transformation of DAO from the UDC system into a site-specific scenario and task-specific system, combined with agility, focus, focus, focus, and convergence (i.e. AFC) smart social systems. DAO can also build on ACP's description of parallel loading systems, predict intelligence, and steering intelligence functions [53], and promote DAO's parallel intelligence [54]. In addition, consideration will be given to combining existing corporate systems with the advantages of the DAO, not only to centralize the features, but to optimize the efficiency of the DATU, and to optimize the efficiency of the DAU in an enabling environment.
本文在系统梳理 DAO 发展脉络及研究现状的基础之上,对DAO 的概念和特点进行了清晰界定,进而提出了一个DAO 分析框架(即五层架构模型)。之后选取一个典型的DAO 平台——Aragon 进行了案例分析,并进一步讨论了DAO 目前所面临的问题和下一步可能的研究方向。随着信息技术的快速发展及环境的复杂多变,工业文明背景下组织结构的弊端愈加明显,DAO 为应对组织失灵的问题提供了有益的参考。然而,从基础理论和现实环境来看,DAO 还有很多不足之处,尚无法支持大规模的应用。但随着理论研究的进一步深入以及各种技术手段的进步,这些问题将会逐步得到解决,DAO 亦将会得到更多的实际应用。
This paper clearly defines the concept and characteristics of DAO on the basis of a system mapping of the DAO development veins and the current state of research, and then proposes a framework for DAO analysis (i.e. a five-storey architecture model). After selecting a typical DAO platform, Aragon, case studies have been carried out and further discussions have been made on the current problems faced by DAO and possible next directions for research. With the rapid development of information technology and the complexity of the environment, DAO’s organizational weaknesses in the context of industrial civilization have become more evident, providing useful references to dealing with organizational failures.
注:本文为中国科学院自动化研究所,青岛智能产业技术研究院平行区块链技术创新中心团队参与的最新力作,本文第一作者就职于北京金桐网投资有限公司,本文已发表于智能科学与技术学报。
Note: The first author of this paper, published in the Journal of Smart Science and Technology, is a recent work by the Automated Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, a team from the `strong' parallel block chain of the `strong' Technology and Innovation Centre.
来源:巴比特
Source: Babit
- 数字人民币初露真容,数字人民币初露真容到底是什么?
- DAG也许是真正的区块链3.0
- 区块链科普深入浅出 | 再也没有比这个更全的区块链知识了!
声明:链世界登载此文仅出于分享区块链知识,并不意味着赞同其观点或证实其描述。文章内容仅供参考,不构成投资建议。投资者据此操作,风险自担。此文如侵犯到您的合法权益,请联系我们kefu@lianshijie.com
Statement: The chain world has published this text solely for the purpose of sharing block chain knowledge, which does not mean endorsing its views or confirming its description. The article is for information purposes only. It does not constitute an investment proposal.
注册有任何问题请添加 微信:MVIP619 拉你进入群

打开微信扫一扫
添加客服
进入交流群
















发表评论